How Search Engines Work
Before you try to optimise your website using SEO tactics, it’s important that you understand the basics of how search engines work, and it all starts with a spider.
A Simple Explanation For How Search Engines Work
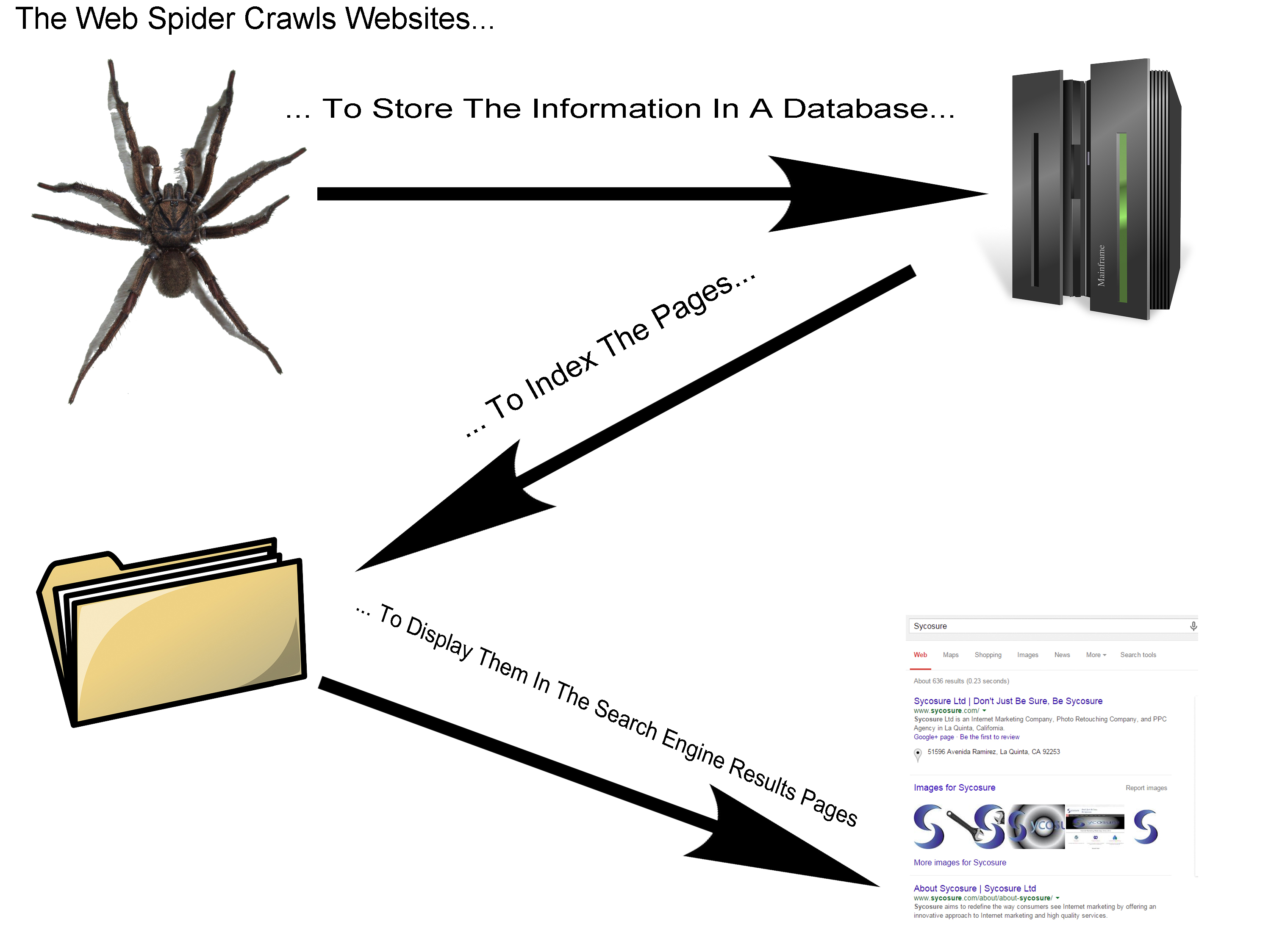
The Web Spider Crawls Websites…
A web spider, also known as a web crawler, is a bot that is programmed to quickly browse websites for URLs and content in order to index them, although this isn’t all they can do. Web spiders can also find and copy content for other uses (in Google’s case, they’ll use it to update information in the Google Knowledge Graph) as well as search previously crawled webpages to find out if they’ve been updated.
… To Store The Information In A Database…
This database also stores information regarding the keywords that you use, links, and images. The information that is put into the web crawlers will then be sorted out to either issue a penalty to a website or submitted to a different database such as the Google Knowledge Graph, Google Maps, or Google Images.
… To Index The Pages…
Once the information has been sorted out, the pages will then be submitted to the search engine index, which will determine what pages will rank, how high up they will rank, what else will be displayed, and who else will be displayed with them.
… To Display Them In The Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs)
The information is displayed only when a user (that’s you) submits a search query (which is what you searched for). This is where the information in the search engines index will be displayed for the user to determine what they will choose to click on. Larger search engines also have intricate algorithms that filter specific results (allowing more relevant content to rank higher in the SERPs based on location, language, and a variety of other factors).